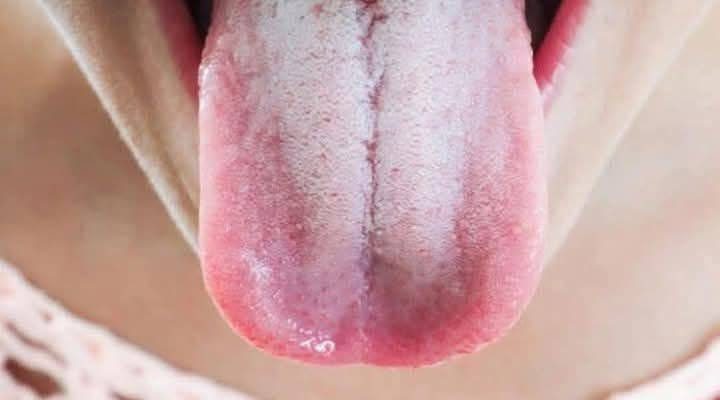
Why Your Tongue Turns White: Causes, Symptoms, and Remedies
Introduction
A white tongue can be alarming, but it is usually a sign of an underlying health issue rather than a serious disease. If you notice your tongue turning white, it might be due to oral hygiene problems, infections, dehydration, or even a more serious health condition. In this article, we will explore the various causes of a white tongue, its symptoms, possible treatments, and preventive measures to maintain good oral health.
Understanding the White Tongue Phenomenon
The tongue is an essential organ responsible for taste, digestion, and speech. A healthy tongue is typically pink with a slight white coating due to natural bacteria and debris. However, when the white coating becomes thick or patchy, it may indicate an underlying problem.
A white tongue occurs when there is an overgrowth of bacteria, fungi, dead cells, or inflammation on the surface of the tongue. Several factors contribute to this condition, ranging from minor oral hygiene issues to serious health problems.
Common Causes of a White Tongue
1. Poor Oral Hygiene
One of the most common reasons for a white tongue is inadequate oral hygiene. When the tongue is not cleaned properly, food particles, bacteria, and dead cells accumulate on its surface, leading to a white coating.
2. Dehydration and Dry Mouth
Lack of sufficient hydration can cause the tongue to appear white. Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health by washing away bacteria and food particles. When saliva production decreases due to dehydration or dry mouth (xerostomia), the tongue becomes coated with a white layer.
3. Oral Thrush (Candidiasis)
Oral thrush is a fungal infection caused by the overgrowth of Candida albicans. It appears as creamy white patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, and sometimes the roof of the mouth and throat. This condition is more common in infants, elderly people, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
4. Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia causes thick, white patches on the tongue and inside the mouth. It is often linked to smoking, alcohol consumption, and chronic irritation from dentures or rough teeth. While leukoplakia is usually benign, it can sometimes be a precursor to oral cancer.
5. Geographic Tongue
This condition causes smooth, red patches with white borders on the tongue, resembling a map. It is a harmless but sometimes painful condition that can be triggered by stress, hormonal changes, or irritation from certain foods.
6. Lichen Planus
Oral lichen planus is an inflammatory condition that affects the mucous membranes in the mouth. It appears as white, lacy patches on the tongue and inside the cheeks. The exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to be an autoimmune disorder.
7. Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Tobacco and alcohol use can lead to a white tongue by drying out the mouth and causing irritation. Smokers are particularly prone to leukoplakia and other oral health issues.
8. Nutritional Deficiencies
Deficiencies in vitamin B12, iron, and folic acid can lead to changes in the tongue’s appearance, including a white coating. These nutrients are essential for maintaining healthy cells in the mouth and tongue.
9. Digestive Issues
Digestive problems like acid reflux, gastritis, and constipation can sometimes manifest as a white tongue. When the digestive system is imbalanced, toxins may accumulate, affecting oral health.
10. Fever and Illness
A white tongue is sometimes associated with fever, flu, or other infections. When the body fights an illness, it may lead to reduced saliva production and an accumulation of bacteria on the tongue.
Symptoms Associated with a White Tongue
A white tongue may be accompanied by additional symptoms, including:
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Dry mouth
- Soreness or burning sensation
- A metallic or unpleasant taste
- Redness or inflammation
- Difficulty eating spicy or hot foods
Treatment and Home Remedies for a White Tongue
1. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
Brushing your teeth twice a day and cleaning your tongue with a tongue scraper or toothbrush can help remove the white coating and prevent bacterial buildup.
2. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water ensures adequate saliva production, helping to wash away bacteria and debris from the tongue.
3. Use Antifungal Treatments (For Oral Thrush)
If oral thrush is the cause of your white tongue, antifungal medications such as nystatin or fluconazole may be prescribed by a doctor.
4. Eat a Balanced Diet
A diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin B12, iron, and folic acid, can prevent nutritional deficiencies that contribute to a white tongue.
5. Avoid Smoking and Alcohol
Reducing or quitting smoking and alcohol consumption can improve oral health and prevent the recurrence of a white tongue.
6. Use Mouthwash or Salt Water Gargle
Antiseptic mouthwashes or a simple salt water rinse can help eliminate bacteria and keep the mouth fresh.
7. Try Probiotics
Probiotics promote good bacteria in the gut and mouth, reducing the risk of fungal infections like oral thrush.
8. Consult a Doctor
If a white tongue persists for more than two weeks or is accompanied by severe pain, bleeding, or difficulty swallowing, seek medical advice.
Preventive Measures for a Healthy Tongue
- Brush and floss daily to maintain oral hygiene.
- Clean your tongue with a tongue scraper.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
- Avoid excessive alcohol and tobacco use.
- Eat a nutritious diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals.
- Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings.
Conclusion
A white tongue is usually harmless and can be easily treated with proper oral hygiene and lifestyle changes. However, if it persists or is accompanied by concerning symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment. Taking care of your oral health not only ensures a fresh mouth but also contributes to overall well-being. Stay hydrated, maintain a balanced diet, and keep up with regular dental visits to prevent a white tongue and other oral health issues.